Why is Soil pH Important?
Understanding soil pH and why it’s important will help you grow healthier plants and improve your yields. Testing your soil is easy, and it’s kind of fun in a Bill Nye the Science Guy kind of way.
As a hobby gardener, you might think that soil pH doesn’t matter…you’re just trying to grow a few cucumbers, right? Well, the impact that soil pH can have on your garden may surprise you, especially if it’s too high or too low.
Let’s say you’re doing everything right. You’re watering correctly and keeping up on pests. You’re feeding your plants organic fertilizer at the right times. You’re double-checking your planting calendar and making sure to plant zone-friendly crops. If after all that and you’re still struggling to produce, it could be a soil pH imbalance.
What is soil pH?
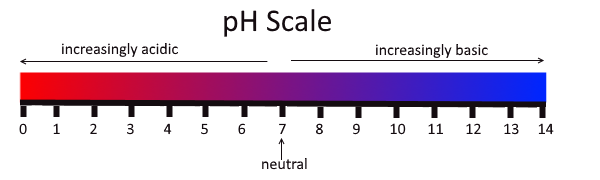
The pH scale is the unit of measurement that determines how acidic or alkaline something is. The scale goes from 0 to 14. A neutral pH is 7. Anything below 7 is acidic and anything above 7 is alkaline.
In the old-timey days, farmers would taste their soil to figure out if it was acidic or alkaline. Acidic soil is described as “sweet” and alkaline soil as “sour.” That’s gross though, and completely unnecessary with today’s scientific advances. Don’t eat your soil, please. I mean, I guess you can if you want. Weirdo.
According to the UF-IFAS, the median pH level of Florida soil is 6.1, but this number varies depending on what part of the state you live in.
Coastal areas have more alkaline soil because they have a higher level of calcium from seashells and limestone. Soil found in pine forests is usually more acidic. Residential gardens are sometimes alkaline because of minerals found in concrete and construction materials.
How Does Soil pH Affect Nutrient Availability?
Incorrect pH can cause all sorts of problems for your plants.
- If the pH is too high or low, it kills beneficial bacteria. This bacteria helps break down organic matter that your plants use for energy.
- Plants can take in soil nutrients easier when the soil is between 5.5 and 6.5 on the pH scale.
- Nutrients will leach out of the soil if it’s too alkaline, causing a deficiency in your plants.
- Highly alkaline soil contains toxic levels of aluminum.
- pH affects soil structure, especially clay. If clay soil is too acidic or alkaline, it gets sticky.
How to Conduct a Soil pH Test
You can test the pH in your garden soil in a few different ways.
Soil pH Testing Meter
The easiest, quickest way to test your soil pH is to use a testing meter. I recommend getting a 3-in-1 which will not only tell you the pH of your soil, but also the moisture level and how much light the plant is getting.
This style of tester is a little like a stake. Just stick it into the ground next to your plant and you’ll get a read-out on the display.
Soil pH Test Strips
You can also test soil pH by using test strips. If you’ve ever tested water in a pool or an aquarium, you’ll find this process familiar.
There will be instructions included with the test strips, so follow those. To give you a general idea, you dissolve some of your soil in water and dip a paper test strip into the solution. The strip will then turn a color that corresponds to a chart that will tell you how alkaline or acidic your soil is.
Sending Your Soil to a Lab
The most accurate way to test your soil is to send it to a lab, although this might not be the preferred method for those looking for instant results. Floridians can contact their local UF/IFAS Extension Office for more information.
What Plants Are Sensitive to pH?
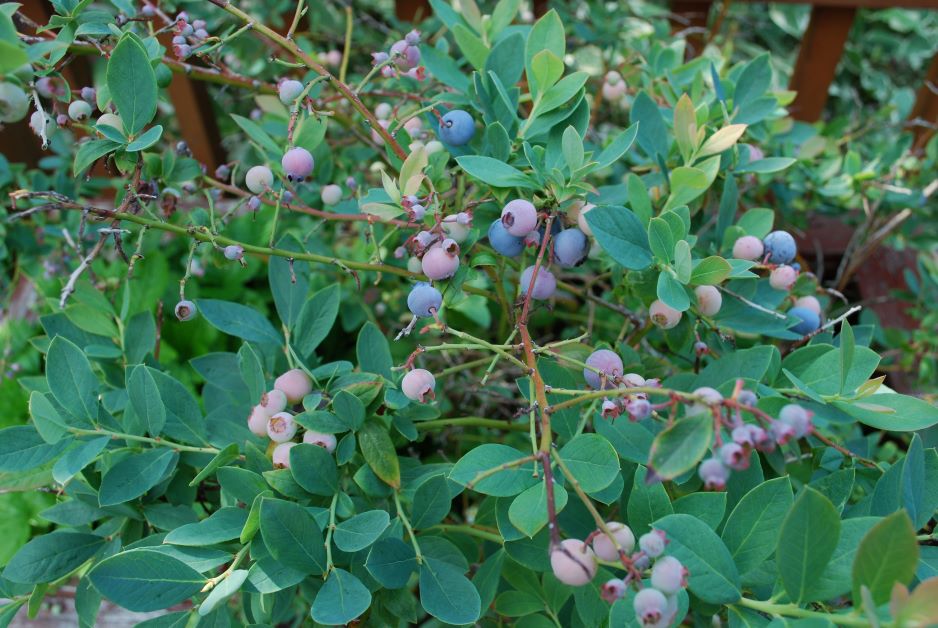

| Plant | Preferred pH |
|---|---|
| Blueberries | 4.5 to 5.5 |
| Strawberries | 5.4 to 6.5 |
| Tomatillos | 5.3 to 7.3 |
| Raspberries | 5.5 to 6.5 |
| Citrus | 5.5 to 6.5 |
| Corn | 5.8 to 7.0 |
| Eggplants | 5.5 to 7.2 |
| Sweet Potatoes | 5.8 to 6.0 |
| Hydrangea | 6.0 to 6.2 |
| Roses | 6.0 to 6.5 |
| Potatoes | 6.5 to 6.5 |
| Watermelon | 6.0 to 6.8 |
| Okra | 6.0 to 6.8 |
| Lettuce | 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Tomatoes | 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Beans | 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Broccoli | 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Cauliflower | 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Cabbage | 6.0 to 7.0 |
| Turnips | 6.0 to 7.5 |
| Peas | 6.0 to 7.5 |
| Beets | 6.5 |
| Squash | 6.5 to 7.5 |
| Peppers | 6.5 to 7.0 |
| Cucumbers | 6.8+ |
How to Raise Soil pH
If you test your soil and see that it’s too acidic, there are a few different ways that you can raise the pH.
Garden Lime
Amend your soil with organic garden lime (limestone). Always follow the instructions printed on the bag, but how much lime you add depends on what type of soil you have:
- Sandy soil – 2 lbs per 100 sq. feet
- Loamy soil – 3.5 lbs per 100 sq. feet
- Clay soil – 5 lbs per 100 sq. feet
It’s better to err on the side of caution when it comes to garden lime – adding too much can burn your plants.
Wood Ash
Although it’s only about 50% as effective as garden lime, wood ash will make your soil less acidic. It also adds nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and potassium to your garden.
It’s important that you use the right kind of wood ash to avoid toxins and heavy metals. Don’t use ash that comes from painted or treated wood, from trees grown close to industrial sites, or from cardboard.
How much wood ash you add depends on the specific needs of your soil. The maximum recommended amount is a 5-gallon pail per 1000 sq. feet.
Wood ash takes some time to work, so you need to add it to the soil 3 to 6 months before planting. On a day that’s not too windy, add ¼ inch of wood ash to the top of your garden beds work it in with a shovel.
You can also dissolve the wood ash in water and make “tea” to water your plants. This’ll help give them a little nutrition over the course of the season.
Baking Soda
Baking soda doesn’t last as long as garden lime, but it’s a cheap fix that’s also gentle on your plants.
Add a tablespoon of baking soda to a gallon of water and add the solution to your garden beds. Although it’s gentle, you should try to avoid getting the solution on the leaves of your plants, so it’s best to use a hand sprayer.
You may have to use baking soda every few months to keep your pH in balance, so test your soil every so often and apply as needed.
How to Lower Soil pH
If your soil is naturally alkaline, studies show that it can be impossible to make your soil more acidic. If you think your soil is alkaline because you added too much lime or wood ash, then you can add garden sulfur or acidifier to balance things out.
Sulfur is strong and can burn your plants, so you should use it sparingly. The maximum recommended amount is 1 lb per 100 sq. feet and you should use it more than once every 8 weeks.
Featured photo credit: Brian Boucheron
Disclaimer: Offbeet-gardener is reader supported. At not additional cost to you, I may receive a commission from purchases made through links in this post.